PRONOUN
Kamis, 24 Maret 2016
0
komentar
Many in fact that we discuss about
pronouns (pronouns) but we begin from an understanding of pronouns (pronouns)
itself.
The word ' prnoun ' is derived from
the Latin ' pronomen ' which means ' to the noun ' (noun) '. Pronouns can also
be interpreted as a sub part of a noun (a noun) that replaces the noun (a noun)
that appears first. But not only as ' subtitutor ' from the obvious noun
(definite noun), pronouns can also refer to the ' quantity ' indifinite
(unknown quantity). While the function of the pronoun itself is to explain who
and what was being talked about by avoiding repetition is confusing.
As indicated in the sense above,
the pronoun we can deduce that the pronoun is divided into two; of the definite
pronoun (object pronoun) and the indefinite pronoun (object pronoun).
1.
Definite
Pronoun
a.
Personal
pronoun
Personal
Pronoun or pronouns are commonly referred to as a person or object is a type of
pronoun which belongs of the definite pronoun. Of the Personal Pronoun, there
are 5 sub divisions which are divided based on the function and position of the
pronoun in a sentence. Fifth subsection personal pronoun:
-
Subjective Pronouns: function as pronouns or subject
the perpetrator to the position before the verb (verb), for example: "He
reads a novel".
-
Objective Pronouns: function as pronoun object with
the position after the verb (verb), for example: "I like Icecream. I like
it. "
-
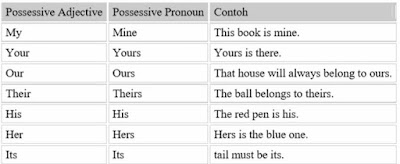
Possesive Adjectives: function as pronouns ownership
position as adjectives (adjective) that describes a noun (noun), for example:
"this is my pen".
-
Possesive Pronouns: function as pronouns ownership
with a position as a noun (a noun), for example: "that is your pen. This
is mine ".
b.
Demonstrative
pronoun
Demonstrative
pronouns or commonly called the pointer is a type of pronoun pronoun which
belongs of the definite pronoun, which we can know things or objects that
replaced it clearly. Demonstrative pronouns used as point-like ' it ' and ' it
' in Bahasa. But in the
English, demonstrative pronouns (pronouns point) is not only influenced by the distance of objects from the speaker, this/this (close) and it/that (much), but is also influenced by the number of objects.
English, demonstrative pronouns (pronouns point) is not only influenced by the distance of objects from the speaker, this/this (close) and it/that (much), but is also influenced by the number of objects.
There are
five demonstrative pronouns: these, those, this, that, and such.
They focus attention on the nouns that are replacing. Examples: “Such was his
understanding.” “Those are totally awesome.”
c. Indefinte pronoun
Indifinite
Person or Thing refers to the lack of clarity of good traits or forms from
people or objects used as pronouns. Indifinite Person or thing is: Someone,
somebody, something, everybody, everyone, everything, anyone, anybody,
anything, onone, onbody, nothing.
These
pronouns do not point to any particular nouns, but refer to things or people in
general. Some of them are: few, everyone, all, some, anything, and nobody.
Example: “Everyone is already here.”
d. Indifinite quantity
Indefinite
Quantity is the amount used to replace people (person) or an object (thing),
for example: All, another, any, both, each, either, a few, less, least, little,
a lot (of), lots (of), many,more,andothers. as we know, the pronoun
(pronoun) presented above is stating pronoun a noun (a noun). In addition to
the Division of the Pronoun (pronoun) as above, there is a Relative Pronoun
pronoun that is used not to replace but to explain, give more information or
describe a noun (a noun) or pronoun (pronoun).
RELATIVE
PRONOUN
If we look, the clause after the '
who ', ' whom ', ' whose ', ' which ' and ' that ' always explain or describe a
Noun (a noun) in the previous clause. As in example a. where clause ' who works
at a garage ' explaining or describing ' a new girlfriend ' which is the noun
(a noun) in the previous clause. Yup, that is indeed a relative pronoun.
Relative pronouns are clause which is prefaced by the words of the question
(who, which, where) used to explain, give more information or describe a noun
(a noun) or pronoun (pronoun)
The above example represents five
of the Relative Pronoun that is some kind of ' who ', ' whom ', ' whose ', '
which ' and ' that '. To the five types of relative pronoun is the author
explain below;
1.
who
Who is kind of relative pronoun used to explain, inform or
describe the PERSON in the previous clause. As in example a. where ' who works
in a garage ' explain ' a new girlfriend '. Who could be used to as a subject
or object.
Let us consider again the example a. above. In fact the
sentence ' He has got a new whoworks in a garage his grilfriend ' originally
consisted of two sentences, namely:
He has got
a new his grilfriend.
[She] works
in a garage.
The second sentence then the merged
by replacing the second sentence of the subject (she) and the ' who '. In this
case the position of the World Health Organization be subject which replaced
the previous position of the subject, she. Relative pronoun who as subject
always replaces the subject as she, he, we, they, etc.
While in this sentence ' His
girlfriend who I met yesterday is on vacation. ' which actually consists of two
different sentences:
His girlfriend is on vacation.
I met [her]
last night.
Describes the position of who as
object due to replace the position of the object in the second sentence of
(her) with menabahkan information ' is on vacation '. Relative pronoun who as
object always replaces the object like his, her, them, you, etc.
2.
Whom
In fact the use of whom is unusual
in daily communication and more leaning to infromal. But there is no harm if we
know and use it in our communication. The actual use of the alternative of whom
who as object. Consider the example below:
His
girlfriend who I met last night is on vacation.
His
girlfriend whom I met last night is on vacation.
The meaning of the two examples
above are actually the same. But the use of the who in the first instance is
more regular and formal while whom on the second sentence is not used commonly
and informally.
3.
Whose
If who and whom replaces the
subject (he, she, they, etc.) and object (his, her, their, etc.), relative
pronoun ' whose ' replaces the possesive pronouns (her, his, your, their,
etc.). Let us consider the above example c. ' I saw a girl whose hair came down
to her waist. ' actually consists of two sentences:
I saw a
girl.
[Her] hair
came down to her waist.
4.
That/which
Relative pronoun That/Which used to
replace objects in the relative clause. As in example d. and e. above:
This is the
key.
[The key]
opens the garage.
be: This is the key that opens the garage.
I forget
most of the films.
I see
[films].
be: I forget most of the films which I see.
5.
When/where/why
In addition to the five realtive
pronoun above, there are three other types i.e. Where, When and Why. Where and
When can explain relative clauses after the noun (verb) that refers to the
place and time. As shown in the following example:
I live in a
town.
[There]I
was born.
Be: I live in a town where I was born.
I will
never forget the day.
[The day] I
first meet you.
Be : I will never forget the day when I first met you.
While the relative pronoun used to
Rev for a reason. Example:
I know ther reason.
[The reason] you love her.
Be: I know the reason why you love
her.
A.
Possesive
Adjective
Posseisve Adjective, yup from the
name alone we can see that the pronoun (pronoun) contains proprietary nature of
the adjective (adjective) are always followed by a Noun (a noun) and not be
able to stand on its own. Always follow by a Noun (a noun) is the hallmark of
the possessive adjective and usage patterns.
Friends can note the possessive
adjective (my, our, your, their, and his, her, its) in the example above is
always followed by a noun (a noun) as: ' my ', ' pen your pen ', ' our home ',
' their decision ', ' his ' hobby, ' her favorite food ' and its ' wings '.
Posseisve Adjective also can not stand on its own without a noun (a noun) that
accompany. We can't form a sentence like this: My is red. Cell is blue.
B.
Possesive
Pronoun
Different possesive adjective is
always followed by a noun (a noun) and not be able to stand on its own without
it, Possessive Pronoun can stand on its own without being followed by a noun (a
noun). Yup, Possessive pronoun is including the noun (a noun) itself.
Possessive Pronoun (mine, yours,
ours, theirs, his, hers, and its) in the example above could stand alone
without a noun (a noun) that follows.
REFLEXIVE
PRONOUN
Reflexive Pronoun pronoun is a
combination of –self with one of the
personal pronoun or with the impersonal pronoun one. The most common use of the
reflexive pronoun is as an object that “ reflects back” to the subject in other
words, it has same identity as the subject.
- Marcella Frank (1972: 22)
Reflexife Pronoun is a pronoun used
to refer to objects that reflect back (reflects back) the subject or
perpetrator. In other words the reflexive pronouns are talking about activities
(action) in which subject and object is the person or thing that is the same.
consider the example below:
I see myself on the mirror.
The door opens itself.
Formation
Of Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexife Pronoun can be created by
adding the words ' – self ' (for single/singlar) – or ' selves ' (the plural
noun to plural) on objective personal pronouns ' my ', ' your ', ' him ', ' her
', ' it ', ' our ', ' them '.
Indefinite
Pronoun
Indefinite Pronoun is a pronoun
that refers to the person (person) or an object (thing) that it is not obvious
are good quality (or shapes) or quantity (amount). Indefinite Pronoun is
divided into two: the Indefinite Person or Thing (referring to the lack of
clarity or the shape of a person or thing) and Indefinite Quantity (referring
to the lack of clarity the amount).
Indefinite Person or Thing
As the explanation provided above,
Person or Thing Indifinite refers to the obscurity of good traits or forms from
people or objects used as pronouns. Below the author has already put in the
form of any pronoun table are included in the Indefinite Pronoun or Thing.
Note: the Indefinite person or
thing above is counted single objects (singular)
Example:
o I need
somebody to help me.
o Everything runs well.
o Could
anyone answer my question?
o Nobody can
stand agints nature.
The word of somebody, everything,
anyone, and nobody above refers to the person or object that is not clearly
characterized and forms the Foundation of the General pronoun.
Indefinite Quantity
From the word quantity above which
has a number of meanings, we can already figure out that Indefinite Quantity is
the amount used to replace people (person) or an object (thing).
Words which belong to the Indefinite Quantity is ;
All, another, any, both, each, either, a few, less, least, little, a lot (of), lots (of), many, more, most, much, "neither, none, one, other (s), plenty (of), several, some are.
All, another, any, both, each, either, a few, less, least, little, a lot (of), lots (of), many, more, most, much, "neither, none, one, other (s), plenty (of), several, some are.
Example:
o One student
should hold this and the others clean the windows.
o Every
person should have a plane in their life.
o All cars
will be washed today.
o Many women
marry at age 21.
reference:
http://www.grammarbook.com/grammar/pronoun.asp
http://www.edufind.com/english-grammar/pronouns/
Baca Selengkapnya ....